Table Of Content

In 1328, Charles IV of France died without a male heir. Queen Isabella made a claim to the throne of France on behalf of her son Edward, on the grounds that he was a matrilineal grandson of Philip IV of France. However, the precedents set by Philip V's succession over his niece Joan II of Navarre and Charles IV's succession over his nieces meant that the senior grandson of Philip III in the male line, Phillip of Valois, became king. Not yet in power, Edward paid homage to Phillip as Duke of Aquitaine. The House of Plantagenet that ruled England from 1154 to 1485, had fourteen kings from the Lancaster House and the House of York.
House of Plantagenet Conflicts

Henry VII, a Lancastrian, became king of England; five months later he married Elizabeth of York, thus ending the Wars of the Roses and giving rise to the Tudor dynasty. The Tudors worked to centralise English royal power, which allowed them to avoid some of the problems that had plagued the last Plantagenet rulers. After Edward’s death, Richard, Duke of Gloucester, shunted aside his nephew who could rightfully claim the throne as Edward V, and gained the ire of many Yorkists when he was crowned King Richard III. Disaffected Yorkists, previously defeated Lancastrians, and French allies threw their support to Henry Tudor, who defeated Richard III at the Battle of Bosworth Field in 1485 and was proclaimed King Henry VII.
Angevins
In the 15th century Henry VI was actually crowned king of the French in Paris. The family maintained close links with the Holy Land through the crusades. Only after 200 years did English become the official language of law and parliament, and even by the time of Geoffrey Chaucer, most sophisticated courtiers still spoke and corresponded in French. Fourteen kings of England belonged to the royal house of Plantagenet.
What was the House of Plantagenet?
King Henry II of England was the son of Geoffrey Plantagenet. Henry became the successor to the throne of England and hence began the dynasty of Plantagenet. Henry II had three royal lines which continued as it is till Edward III became the king. The House of Plantagenets was originally from the Counts of Anjou. The Plantagenet dynasty was established in the tenth century by Fulk I of Anjou. They ruled England from 1154 to 1485 for 331 years, providing England with 14 greatest kings.
Henry V
DNA Evidence Casts Doubt on Richard III's Claim to the Throne - Mentalfloss
DNA Evidence Casts Doubt on Richard III's Claim to the Throne.
Posted: Tue, 02 Dec 2014 08:00:00 GMT [source]
If you discover one of these, please send it to us, and we'll add it to our database of clues and answers, so others can benefit from your research. Basically, the coat of arms is a unique design represented on the shield of the knight. The design for each individual was unique and that one person only has the right to that coat of arm during his whole life. He may be allowed to pass that coat of arm to his descendants which later will be the coat of arms of the family. The symbols that are displayed on the coat of arms depicts the person’s achievements.
Richard’s reign is unusual in thathe spent little time in the country. Richard went on Crusade, getting close to the holy city of Jerusalem. He became embroiled in a dispute with the Austrians which led to his imprisonment and being held to ransom. This created a large financial burden for the country, not helped by plotting by his brother, John and the French. The House of Plantagenet ruled England in some form or another from the reign of Henry II, beginning in 1154, until the House of Tudor came to power when Richard III fell at the Battle of Bosworth Field in 1485. The War of Roses that happened between 1455 to 1485 was a series of civil wars fought between the House of York and the House of Lancaster.
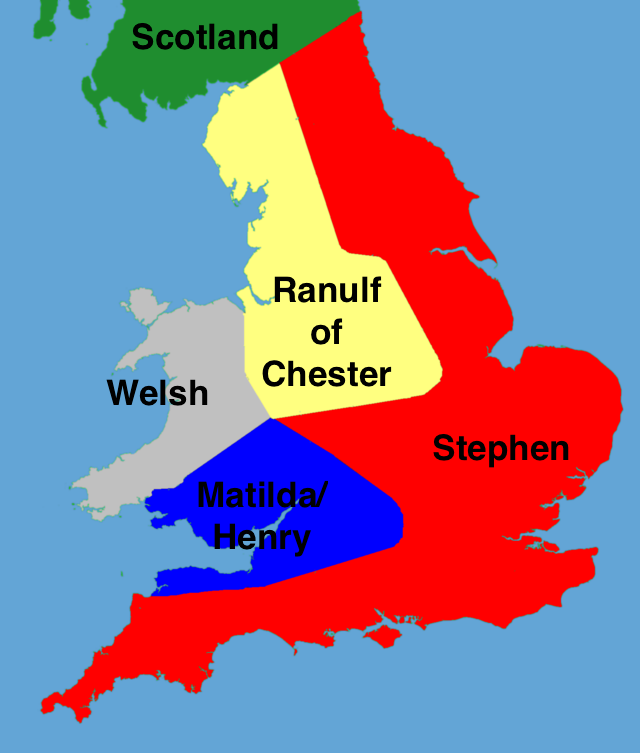
Edward III’s numerous children and their marriages greatly affected English history. Edward’s heir, the “Black Prince,” left an only son, who succeeded his grandfather as Richard II, on whose death (1399) this line became extinct. Lionel, the next surviving son of Edward III, left an only child, Philippa, who married the earl of March, in whose heirs was the right to the succession. The rivalry between the House of Plantagenet's two cadet branches of York and Lancaster brought about the Wars of the Roses, a decades-long fight for the English succession. It culminated in the Battle of Bosworth Field in 1485, when the reign of the Plantagenets and the English Middle Ages both met their end with the death of King Richard III.
The life, scandals and loves of Princess Margaret
His accession was te result of agreements that brought to an end the civil war between Stephen and Henry’s mother, Matilda. His reign was marked by the murder of Thomas Becket and feuds between himself and his sons, Richard and John. Between their son and Henry VI (grandson of Henry IV) and the sons and heirs of these rivals was fought out the dynastic struggle known as the Wars of the Roses, which proved fatal to several members of both houses. It did not end until the last Yorkist king, Richard III, was defeated at Bosworth Field in 1485 by Henry Tudor, who became Henry VII and founder of the house of Tudor. Although his earldom was forfeited, Richard (the father) was not attainted, and the four-year-old orphan Richard was his heir.
The different Plantagenet monarchs had hugely different levels of success in this regard. By the end of the dynasty’s rule, the nations of the British Isles and France were formed in much the way that we now see them on the map. Although well established, the surname Plantagenet has little historical justification. It was not, however, a hereditary surname, and Geoffrey’s descendants in England remained without one for more than 250 years, although surnames became universal outside the royal family.
The minority rule of Henry VI saw leading nobles ruling. He was not a strong figure and court began to disintegrate as factions squabbled. Henry’s rule was then briefly reinstated as the War of the Roses swung in favour of the House of Lancaster. Edward IV returned though, defeating Henry’s forces, organised by his wife, Margaret of Anjou and the Earl of Warwick and regaining the throne. Henry II became king following the death of King Stephen.
Richard III was the last member of the Plantagenet family who was killed in 1485. There have been some more descendants through a few members of the Plantagenet dynasty. The first true armigerous dynasty of England was the Plantagenets. The coat of arms of this royal family signified the arms of England specifically the arms of the royal house of England. Edward II’s unhappy reign put the first real chink in the Plantagenet armour but the steady rule of his son, Edward III, turned England into a powerhouse once again. When Richard II succeeded in 1177, there were high hopes that the Plantagenet dynasty was heading for its most glorious time of all.
Richard had himself crowned King Richard III (ruled 1483–85). Henry V (ruled 1413–22) emerged as one of the great English warrior kings of the Middle Ages. He scored several victories against the French, in particular at the Battle of Agincourt (1415), when his troops beat a much larger French force. Henry V eventually united the crowns of England and France through his marriage to the French princess Catherine of Valois.
The young queen moved to Windsor but her husband’s increasing political problems turned her into a potential target and she spent the last part of his reign being moved around England for her own safety. Anne sometimes bore her father, Warwick the Kingmaker's, full achievement, however at other times she also bore the arms of Neville without difference. Executed in 1478 at the orders of King Edward IV (his own brother), for having designs on the throne. The usual forms of address for a king for much of the Plantagenet era were ‘your highness’ and ‘your Grace’.
The Real History of Game of Thrones: Tyrion Lannister - Den of Geek
The Real History of Game of Thrones: Tyrion Lannister.
Posted: Fri, 17 May 2019 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The early Plantagenet kings struggled for power with the Roman Catholic Church and the English nobles. By the time of King John’s reign, a group of powerful men known as barons had joined together to try to limit the king’s power and to make him rule according to law. In 1215 they forced him to sign a document called the Magna Carta (or “Great Charter”). This limited the rights of the king and protected the rights of his subjects. However he died unexpectedly while his heir was a baby.

No comments:
Post a Comment